COST-BENEFIT ANALYSIS
Posted MAY 21 2015 by THIAGO.
Alternating current (AC) is the main driving force in the industries and residential areas, but for the long transmission line (more than 650 kilometers) AC transmission is more expensive than that of direct current (DC). Technically, AC transmission line control is more complicated because of the frequency. DC transmission does not have these limitations, which has led to build long HVDC transmission lines over the last 40 years. HVDC technology made possible to transfer bulk power over long distances.
Estimate the costs is not a straight forward calculation, because the equipment’s costs are always varying and also it varies from place to place and company to company. For this calculation, the installed cost of each of these items includes cost of materials or equipment, construction, land, material handling, surveys and usually overhead charges.
AC Station Costs
Alternating current switching and substation plant may include the cost of following major items:
-
power circuit breakers,
-
power transformer,
-
disconnect switches,
-
reactors,
-
shunt capacitors,
-
static capacitors,
-
synchronous compensators,
-
series capacitors,
-
buswork,
-
protection and control systems,
-
structures and control houses.
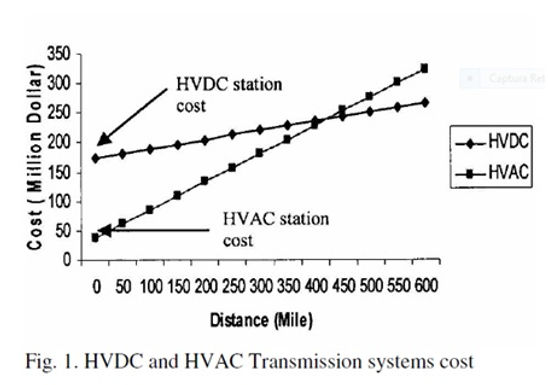
The estimate cost for the circuit breaker and transformer include the approximate cost of related control and protection, buswork, disconnect switches, related structures, and control houses. Total cost for the sending and receiving end AC stations is $37.69 million. All costs are calculated on the basis of year 1985. The cost of electrical and electronic equipments varies time to time; naturally the cost goes down with newer technology. The HVDC and HV AC system consist of not only the equipment cost but also the labor cost, which goes up with the time. If both costs compensate each other, the present cost would be the same as 1985's cost. By taking inflation into account, the costs in 1985 can be converted to the present equivalent cost, and the multiplying factor is 2.19, costing $82.71 million.
AC Transmission Line Costs
AC transmission line needs bigger space and more construction cost than those of DC transmission or the same power capability and comparable reliability. AC transmission line has 3 power carrying conductors where as DC transmission has only two and theses reasons increase the AC transmission line costs significantly. A typical cost for 500 kV AC line is $955/kV-mile. Nelson River Bipole 1 (an electric power transmission system of high voltage, direct current lines in Manitoba, Canada) is 895 km; total transmission line cost is 265.6 million dollars. Total cost for the Nelson River Bipole 1 if AC transmission would be used is 303.29 million dollars.
DC Station Cost and Line Cost
The main equipment of the D.C station is converters and more than 50% costs of HVDC transmission system are related to the converters. The converter stations are the key component to make an economical comparison between DC and AC transmission system. For an AC system the line costs predominate and station costs are small and for the DC system stations costs predominate and line costs are small. Using 1 p.u. = $100/kW, the converter stations cost range is $149.24x106 to $198.28x106. The average is $173.5x106.
The line cost for the DC transmission system is $320 -$370/kV-mile for ±400 to ± 700kV. If $345/kV-mile is taken for the ± 450 kV transmissions line the total line costs for 556.2 miles is $86.3×106. The total cost of DC transmission system for the Bipole 1 is $259.8×106, which is 43.49 million dollars lower than that of AC transmission system.
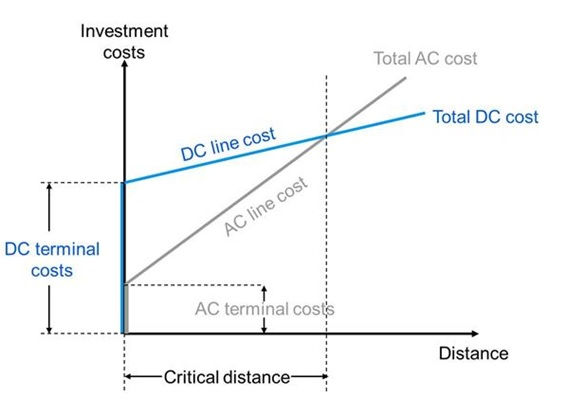
Lower Investment Cost
An HVDC transmission line costs less than an AC line for the same transmission capacity. However, it is also true that HVDC terminal stations are more expensive due to the fact that they must perform the conversion from AC to DC, and DC to AC. But over a certain distance, the so called "break-even distance" (approx. 600 – 800 km), the HVDC alternative will always provide the lowest cost.
The break-even-distance is much smaller for subsea cables (typically about 50 km) than for an overhead line transmission. The distance depends on several factors (both for lines and cables) and an analysis must be made for each individual case.
The break-even distance concept is important, but only one of a number of factors, such as controllability, that are important to consider in choosing an AC or HVDC transmission system.
REFERENCES
MEAH, Kala; ULA Sadrul. Comparative Evaluation of HVDC and HVAC Transmission Systems. IEEE. Access on May 10.
LAZARIS, Lazaros P.. Economic Comparison of HVAC and HVDC Solutions for Large Offshore Wind Farms under Special Consideration of Reliability. Access on May 10.
EDVARD. Analysing the costs of High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) transmission. Posted Aug 6 2014 in High Voltage, Transmission and Distribution. Access on Abril 25.
Article Tags:
HVDC, cost benefit analysis, station costs, investment costs, transmission lines, comparison, budget, financial analysis.